Pink dolphins: an endangered species
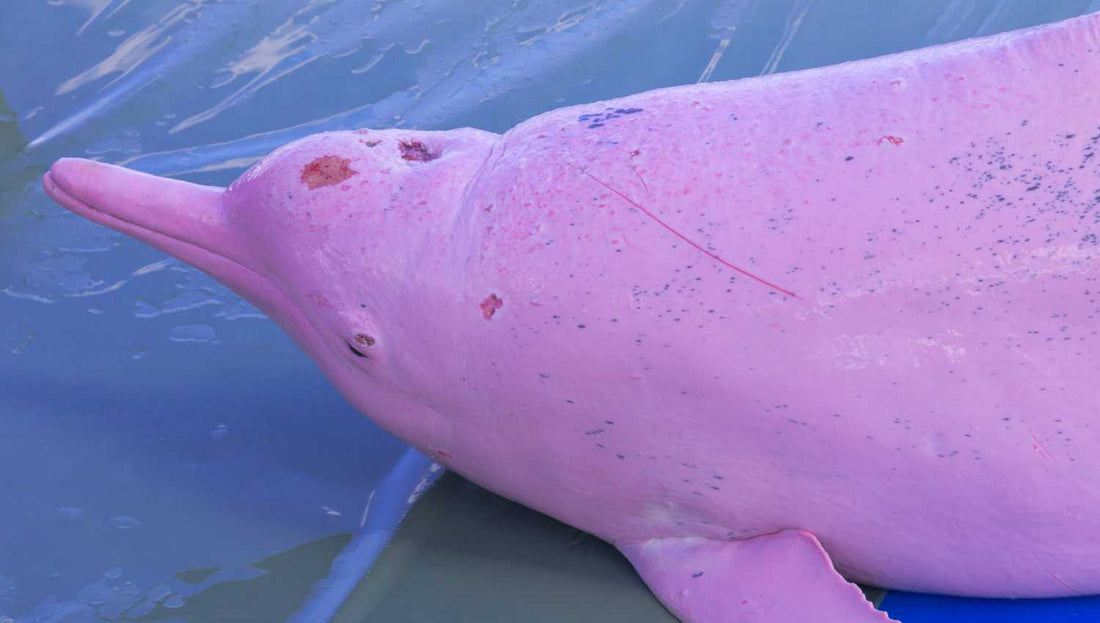
Pink dolphins are a rare and fascinating natural phenomenon. They are also known as albino dolphins or Risso 's dolphins, as they belong to the species Grampus griseus. Although all dolphins are considered magnificent animals , pink dolphins have an even more stunning appearance due to their unusual color.
The pink color of dolphins is caused by a lack of pigmentation , known as albinism . This lack of pigmentation not only affects the color of their skin , but also that of their eyes and fins . However, despite their unique appearance, pink dolphins are able to live and reproduce like normal dolphins. Unfortunately, due to their rarity , they are often the target of poachers and hunters who seek to capture them for display in marine parks or sell them to private buyers .

Presentation of the pink dolphins
It is important to note that this unusual color of their skin makes them more visible to predators , and thus, they may be more exposed to natural hazards .
Pink dolphins are majestic and fascinating animals that attract attention wherever they go, but it is important to remember that their unique appearance does not make them invincible and that they need our protection to continue to exist.
Why are pink dolphins considered an endangered species?
It is difficult to say with certainty how many pink dolphins exist in the world. The population is very rare and there is little data available on their exact numbers. Sightings of pink dolphins have been reported in waters around California, Japan, the Mediterranean, the China Sea , Africa, but it is difficult to say how many specimens actually exist.
Scientists and observers seek to learn more about this unique species to better understand their geographic distribution and numbers. It is generally accepted that their population is very low and decreasing, so it is important to continue to protect the remaining populations of pink dolphins in order to preserve this unique species and to avoid their extinction.
Do pink dolphins still exist?
There are still pink dolphins living around the world, but they are very rare. Sightings of pink dolphins have been reported in waters around California , Japan , the Mediterranean , the China Sea , Africa , but it is difficult to say how many specimens actually exist.
Their albinism makes them particularly vulnerable to UV rays and makes them more visible to predators. These factors, combined with illegal capture for marine parks and incidental fishing, have led to a decline in their overall population . It is important to continue to protect the remaining populations of pink dolphins in order to preserve this unique species and to prevent their extinction.
-
Sporadic sightings: Although pink dolphins are very rare, they still exist around the world. Sightings of pink dolphins have been reported in waters around California, Japan, the Mediterranean, the China Sea, Africa, but their population is difficult to accurately assess. Scientists and observers seek to learn more about this unique species to better understand their geographic distribution and numbers.
-
Natural and human factors: Pink dolphins are affected by a range of natural and human factors that impact their population. Their albinism makes them particularly vulnerable to UV rays and makes them more visible to predators. Illegal capture for marine parks and incidental fishing are major factors that have led to a decline in their overall population.
-
The need to protect: Pink dolphins are a unique species and it is important to continue to protect remaining populations to prevent extinction. Protection programs target reducing illegal capture , incidental fishing , marine pollution and climate change that impact these animals. Action to protect pink dolphins and their natural habitat is essential to preserve this unique species for future generations.
The pink Amazonian dolphin
Amazonian pink dolphins, also known as pinkbuds , are a group of river dolphins found primarily in the fresh waters of the Amazon River and its tributaries . They have a unique appearance and are considered one of the most endangered dolphin species in the world. This article will examine the physical and behavioral characteristics of Amazonian pink dolphins, their habitat and their conservation status.
Physical and behavioral characteristics
Amazonian pink dolphins have a distinct appearance with a pale pink to reddish coat which gives them their name. They have a broad head and short snout , as well as a rather small dorsal fin. They are approximately 2 meters long and weigh approximately 150 kg. Amazon pink dolphins are social animals and often travel in groups of 10 to 20 individuals. They are very active and can jump high out of the water and perform acrobatics.
- Physical description
Amazonian pink dolphins are recognizable by their pale pink to reddish coat which gives them their name. They also have a broad head and short snout, as well as a rather small dorsal fin. They are approximately 2 meters long and weigh approximately 150 kg . Their physical appearance distinguishes them from other species of river dolphins which tend to have a darker color.
- Social behavior
Amazonian pink dolphins are social animals and often travel in groups of 10 to 20 individuals . They are also very active and can jump high out of the water and perform acrobatics. They are also very curious and can approach boats and humans to observe them. Groups of Amazon pink dolphins are often led by an alpha female who makes decisions for the group.
- Eating behavior
Amazonian pink dolphins feed primarily on fish and crabs , which they hunt using their sonar to locate their prey. They may also eat shellfish. Amazon pink dolphins are also known to use tools to hunt, such as using branches to capture crabs. Groups of Amazonian pink dolphins may also work together to hunt larger prey.
Habitat
Amazon pink dolphins live primarily in the fresh waters of the Amazon and its tributaries, although they can be found in other rivers in South America . They prefer calm , shallow waters with abundant vegetation . They feed on fish and crabs , which they hunt using their sonar to locate their prey .
Causes of the threat to pink dolphins
Pink dolphins are considered an endangered species due to several factors threatening their population. Illegal capture for marine parks, accidental fishing, marine pollution and climate change are the main causes of the threat to pink dolphins.
Poaching and capture for marine parks
Illegal capture for marine parks is one of the main causes of the threat to pink dolphins. Their unique appearance makes them particularly sought after by establishments looking to attract visitors, unfortunately these captures can cause irreparable damage to pink dolphin populations, leading to a decline in their overall population.
Capturing pink dolphins for marine parks and aquariums is illegal in some countries, but unfortunately it continues to be a problem in other parts of the world. Illegal captures can cause injury and stress to animals, and can even result in death during capture attempts. Captured pink dolphins are often subjected to inappropriate living conditions, with restricted confinement spaces and a lack of adequate veterinary care.
Pink dolphin protection programs aim to reduce these illegal captures by working with local authorities and organizations to strengthen laws and regulations on the capture of this endangered species. Awareness campaigns and collaboration with coastal communities are also used to educate fishermen and tourism about the need to protect pink dolphins.
It is important to continue to protect pink dolphins from illegal capture and commercial exploitation to ensure the survival of this unique species for future generations.
Accidental fishing
Fishing nets used in incidental fishing are often gillnets and longlines , which can catch large quantities of fish or shellfish. Unfortunately, these nets can also capture dolphins and other marine life , including pink dolphins. Dolphins captured by accident can be seriously injured or killed by nets or ropes, and even if released, they can suffer long-term physical and mental damage that can affect their ability to feed and reproduce.
Marine pollution
Climate changes
Climate change is a threat factor for rosy dolphins, as for many other marine species. Climate change impacts their habitat and food , with changes in water temperatures , currents and salinity levels that can affect the distribution of species that constitute their food, or cause disruption in their natural habitat .
Climate change can also cause disruptions in weather systems, such as hurricanes, storms and heat waves , which can cause damage to pink dolphin habitats and affect populations of fish and shellfish that make up their diet. Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, can also cause illness and hormonal disruptions in pink dolphins.
Pink dolphin conservation programs include population monitoring to assess the impact of climate change. Research programs on pink dolphins and their habitat also make it possible to better understand the impacts of climate change on this species and to develop appropriate conservation strategies.
It is important to note that in addition to these direct effects on pink dolphins, climate change also has indirect consequences on this species via impacts on the ecosystems and species that surround them, such as dolphin prey or predators. roses.
It is therefore important to continue to monitor pink dolphin populations and their habitat in order to better understand the impacts of climate change and implement appropriate conservation strategies. It is also important to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to limit climate change and protect pink dolphins and their natural habitat.

The effects of the decline in the pink dolphin population
The decline in the pink dolphin population has significant effects on the marine ecosystem and the entire ecosystem .
First of all, a decline in the pink dolphin population can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems. Pink dolphins play an important role as predators and can impact populations of fish and shellfish that constitute their food. The decline in the pink dolphin population may also impact the populations of their predators and competitors, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, the loss of a species has significant ecological consequences. Pink dolphins are a unique and interesting species, their disappearance would impact marine biodiversity and the people who love and study them.
Finally, the loss of a unique species can have economic consequences, particularly for fishing and tourism activities, which can be affected by the loss of an emblematic species.
Impact on the marine ecosystem
The disappearance of pink dolphins could have a significant impact on the marine ecosystem . Pink dolphins are important predators that play a crucial role in regulating fish and shellfish populations. They help keep populations in balance by eliminating weaker individuals and controlling the levels of food available to other species.
Additionally, pink dolphins are social animals that live in large groups, so they can have a huge impact on fish and shellfish populations even in areas where they are not very numerous. They form important schools for certain species of fish such as sardines , anchovies and herring .
The disappearance of pink dolphins would also have an impact on other cetacean species that are linked to them through feeding relationships. Orcas and bottlenose dolphins, for example, often prey on pink dolphins. Without these prey, they might be forced to hunt other species, which would impact the ecosystem .
There are also side effects that come from the disappearance of pink dolphins, they are indicators of water quality and the health of the marine ecosystem , so their disappearance could mean that other problems arise in the region.
Loss of biodiversity
The disappearance of pink dolphins and other animal species is linked to the loss of biodiversity, which is defined as the variety of life on Earth. Biodiversity includes the diversity of living species, ecosystems and genes.
Biodiversity loss is a global problem that has serious consequences for the environment, human health and economic well-being. Ecosystems and animal species are closely linked, and when some species disappear, it can disrupt the balance of ecosystems and cause changes in the populations of other species. It can also lead to disruptions in food chains and biochemical cycles, leading to long-term consequences for the ecosystem.
It is important to protect pink dolphins and other species to preserve biodiversity. Conservation measures include reducing pollution, protecting habitats, regulating hunting and fishing, restoring ecosystems, and providing education to raise awareness of the issues. It is also important to reduce human activities that negatively impact the environment, such as deforestation, intensive agriculture and mining.
Consequences for coastal communities that depend on fishing
The disappearance of pink dolphins could have significant consequences for coastal communities that depend on fishing. Pink dolphins play an important role in the marine food chain by feeding on fish and squid, which are often species targeted by fishermen. If pink dolphin populations decline, it is possible that fish and squid populations will increase, which could lead to increased competition for resources between dolphins and fishermen.
Additionally, pink dolphins are often used to spot schools of fish, and fishermen often use the dolphins' movements to locate schools of fish. If pink dolphins disappear, fishermen may have less success locating schools of fish, which could lead to a drop in their yield.
Finally, pink dolphins are often used for coastal tourism, and their disappearance could have a negative impact on local economies that rely on wildlife tourism. People come specifically to see pink dolphins and their absence could deter visitors from going to these areas, leading to lower visitor numbers and revenue for local tourism businesses.
It is important to emphasize that the protection and conservation of pink dolphins is crucial to preserve these species as well as the maritime ecosystems that depend on them, and to ensure the sustainability of economic activities linked to fishing and tourism that depend on them.
Current and future conservation measures
There are several current and upcoming conservation measures to protect pink dolphins and their habitat. Here are some examples :
-
Creating protected areas: Authorities can create protected areas where human activities (such as fishing and resource extraction) are regulated or prohibited in order to protect pink dolphins and their habitat.
-
Fishing regulations: Authorities can also regulate fishing activities to reduce negative impacts on pink dolphins. For example, they may limit the types of nets and traps used, or impose catch quotas for certain species of fish and squid that are prey to pink dolphins.
-
Awareness: It is important to raise awareness among fishermen, boaters and the public about the impacts of human activities on pink dolphins and current conservation efforts. This may include information campaigns, training for fishermen and boaters, and educational programs for schools and community groups.
-
Research: Research on pink dolphins is needed to better understand their biology, their food and habitat requirements, and the factors that threaten their survival. The results of this research can then be used to develop effective conservation strategies.
-
International cooperation : The conservation of pink dolphins requires international cooperation because these animals can migrate great distances and their habitat spans several borders. It is therefore necessary to work with international organizations and governments of other countries to develop effective conservation policies and programs.
It is important to note that the conservation of pink dolphins is an evolving process; it is necessary to continue to monitor dolphin populations, study changes and adapt conservation strategies based on the results.
Population protection and surveillance programs
There are several programs to protect and monitor pink dolphin populations around the world. Here are some examples :
-
Population monitoring programs : These programs involve regularly monitoring pink dolphin populations in designated areas to assess their abundance, distribution and mortality. The data collected can be used to develop effective conservation strategies.
-
Individual marker programs : These programs involve marking pink dolphins individually with distinctive markers (such as tattoos or rings) to identify them at each sighting. The data collected can be used to track dolphin movements, social relationships and reproductive rates.
-
Acoustic recognition programs : These programs use underwater recorders to record the calls of pink dolphins. The data can be used to assess the population density, distribution and population trends of pink dolphins in the study areas.
-
Counting Programs : Counting Programs can use aerial observation to count pink dolphin populations in specific areas, and these data can be used to assess the abundance and distribution of pink dolphin populations.
-
Reintroduction programs: These programs involve releasing captive individuals into areas where pink dolphin populations have been severely reduced. The data collected can be used to evaluate the success of these reintroduction programs.
It is important to emphasize that these pink dolphin population protection and monitoring programs are not unique ways to protect pink dolphins, but rather they are tools for a better understanding of the current population status and trends. This allows managers to make informed decisions to protect pink dolphin populations and their habitat.
Awareness campaigns
There are several awareness campaigns that aim to educate fishermen, boaters, tourists and the general public about the impacts of human activities on pink dolphins and ongoing conservation efforts. Here are some examples of awareness campaigns:
-
Awareness campaigns among fishermen: These campaigns aim to make fishermen aware of the impacts of their activities on pink dolphins and to encourage them to adopt more sustainable fishing practices. These campaigns may include training on fine mesh nets, traps and other types of fishing gear that can cause injury or mortality to pink dolphins.
-
Awareness campaigns for boaters: These campaigns aim to make boaters aware of the impacts of their activities on pink dolphins and to encourage them to adopt responsible behavior at sea. These campaigns may include information on navigation rules and sailing distances. safety to be respected to avoid collisions with pink dolphins.
-
Awareness campaigns among tourists: These campaigns aim to make tourists aware of the impacts of their activities (such as dolphin watching) on pink dolphins and to encourage them to adopt responsible behavior during their tourism activities at sea. These Campaigns can include information on best practices for observing pink dolphins while respecting their welfare.
-
Public awareness campaigns: These campaigns aim to raise awareness among the general public about the impacts of human activities on pink dolphins and about ongoing conservation efforts. These campaigns can include information about the threats facing pink dolphins and the actions individuals can take to help conserve these animals.
These campaigns can take different forms such as information disseminated via the media, communications campaigns on social networks, presentations in schools and community groups, or even poster publications or information brochures.
International collaboration for the conservation of pink dolphins
Conservation of pink dolphins requires international collaboration because these animals can migrate great distances and their habitat spans multiple borders. It is therefore necessary to work with international organizations and governments of other countries to develop effective conservation policies and programs.
Here are some examples of international collaborations for the conservation of pink dolphins:
-
International Conventions: There are several international conventions that deal with the conservation of endangered species, such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora ( CITES ) and the Convention on Biological Diversity ( CBD ). . Countries that sign these conventions commit to adopting effective conservation policies and programs to protect endangered species, including pink dolphins.
-
Regional agreements: There are regional agreements for the conservation of pink dolphins between countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, the Baltic Sea and the Atlantic, which have been concluded to protect populations of pink dolphins in these regions. These agreements include monitoring and protection programs for pink dolphins, as well as awareness programs for fishermen and boaters.
-
International organizations: There are international organizations working for the conservation of pink dolphins, such as the Convention on the Conservation of Dolphin Populations of the Mediterranean and Atlantic Sea ( ACCOBAMS ) or the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of North Atlantic (ACCOBAMS) whose mission is to promote the conservation of pink dolphins and other cetacean species in the regions concerned.
-
Cooperation between NGOs : Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play an important role in the conservation of pink dolphins, and it is common to see NGOs working together to carry out awareness campaigns, research programs, and actions. protection on dolphin populations.
It is important to emphasize that international cooperation is essential to protect pink dolphin populations because these animals can migrate great distances and their habitat spans multiple borders.
Collaboration between different countries makes it possible to put in place effective conservation policies and programs to protect pink dolphins and their habitat, and thus ensure the long-term survival of this species.
Laws and regulations to protect pink dolphins
There are several laws and regulations that aim to protect pink dolphins and their habitat. Here are some examples :
-
National Laws: Each country has its own laws and regulations to protect wildlife, including rosy dolphins. These laws may prohibit certain activities such as hunting or capturing pink dolphins, and may also provide penalties for violations.
-
International conventions: There are international conventions like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which protect endangered species from international trade, such as pink dolphins. Countries that sign these conventions commit to adopting effective conservation policies and programs to protect endangered species.
-
Fishing regulations: There are regulations that aim to protect pink dolphins from the impacts of fishing, such as bans or restrictions on certain types of fishing gear (such as fine mesh nets), or fishing quotas. taken for certain species of fish and squid which are prey to pink dolphins.
-
European Union Directives: There are European Union directives to protect pink dolphins, such as the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive which aim to protect threatened species and habitats and manage human activities which can affect the survival of species.
It is important to emphasize that these laws and regulations are not sufficient to protect pink dolphins, they are tools to better manage the impacts of human activities on these animals and their habitat. However, their effective application often depends on the capacity of governments to enforce them and the measures that have been put in place to enforce them.

Conclusion on pink dolphins: an endangered species
In conclusion, pink dolphins are an endangered species due to human activities that affect their habitat and survival. The main threats to pink dolphins are fishing, impacts of human activity on their habitat, pollution and climate change.
To protect pink dolphins and their habitat, it is important to put in place effective conservation measures, such as the creation of protected areas , fishing regulations, awareness, research, and international cooperation.
It is also important to follow the laws and regulations in place to protect pink dolphins, as well as continue to monitor pink dolphin populations and adapt to ongoing trends. Raising awareness among fishermen, boaters , tourists and the general public is crucial to protect them and to encourage them to adopt more responsible behavior.
International cooperation is also essential to protect pink dolphin populations and their habitat. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of each of us to protect this endangered species and contribute to the conservation of pink dolphins for future generations.
The oceans and natural environments on land are home to many unique animal and plant species. Mammals, reptiles, amphibians, turtles and whales are examples of species that need protection for their survival. The oceans are also home to important plant species, such as coral reefs which are home to unique animal species.
Global warming, pollution and human activities have a devastating impact on many animal and plant species. Nature protection is crucial to preserving these species and their habitat. The International Union for Conservation of Nature ( IUCN ) regularly publishes red lists of endangered species, such as sea turtles, whales and rhinoceroses, to raise awareness of the need to protect these species.
Nature conservation also includes the protection of marine protected areas , which are home to unique species of aquatic flora and fauna. Coral reefs, seas and wetlands are examples of natural environments that support unique species and are threatened by human activities. The captivity of these wild animals in zoos and water parks is also a major concern.
It is important to take measures to protect endangered animal and plant species . Respecting environmental law and participating in nature conservation campaigns are important ways to protect fauna and flora . Regular monitoring of the distribution area of these species is also necessary to assess their number and situation. Ultimately, it is our responsibility to protect this species.